Targeting Options for Google Display Campaigns
When it comes to Google Display Ads, targeting is going to be central to your campaigns’ success.
Unlike Search and Shopping Ads, which rely heavily on keyword-based targeting, Display Ads aren’t being triggered by specific searches. Instead, you tell Google who you want to see your ad (and potentially where you’d like them to see it), and that determines who sees your ad as they’re browsing other websites and apps online.
Without the proper targeting, you’ll struggle to reach the right audiences, and your click-through rates (CTRs) and conversions may stay low as a result, even if your ads are on point.
So in this chapter of our Ultimate Guide to Google Display Ads, we’re going over every targeting option available to you with Display Campaigns and when (and how!) to use them.
Targeting Options Available Through Google’s Display Ads
The first thing we want to do is look at Google Display Ads targeting options.
Makes sense, right?
Once we go over what your targeting options are, it’s much easier to discuss how to set up audience targeting and how to choose targeting criteria for your campaigns.
So, first things first: There are technically six main factors that you can use to tell Google who you want to reach. Let’s look at each one.
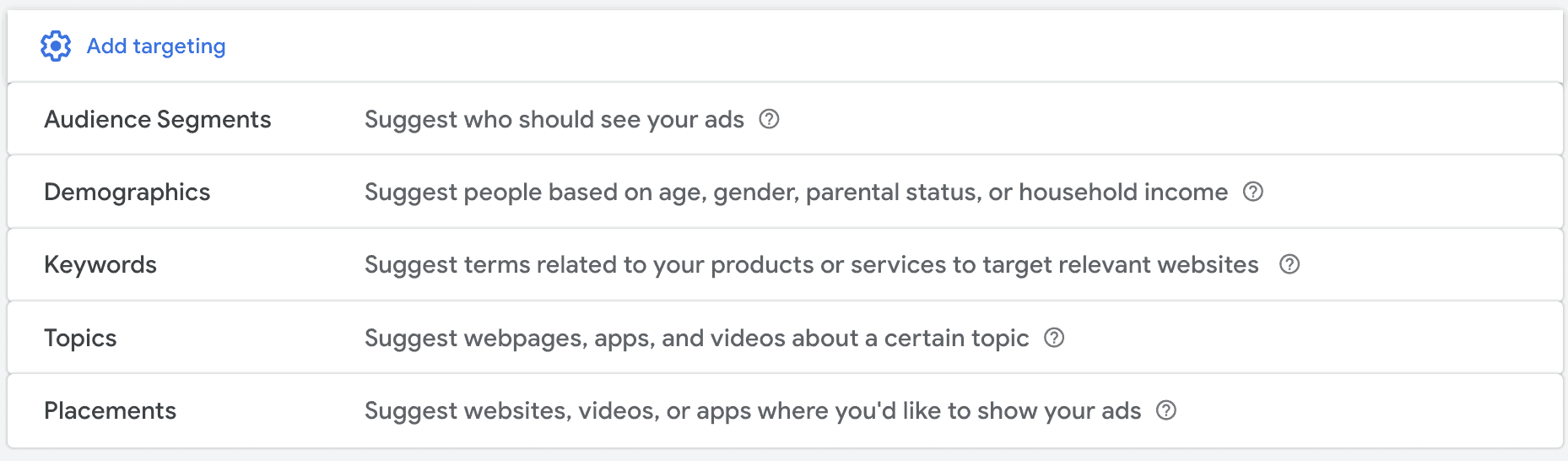
Location & Languages
You may notice that there were only five different types of audience targeting in the image above, but that we said there are six targeting options.
Location and languages (which we’re lumping into one category to keep things simple) are not on the audience targeting page, but it still impacts who sees your ad. So while it’s one of the first decisions you make for your campaign, we’re still including it as an audience-targeting option.
You can either include users in a certain location or exclude users in a certain location. So if you want to only show your ad to users who are in Tuscaloosa, Oklahoma, you can, and you can choose to exclude users from Tuscaloosa, Oklahoma from seeing your ad, too.
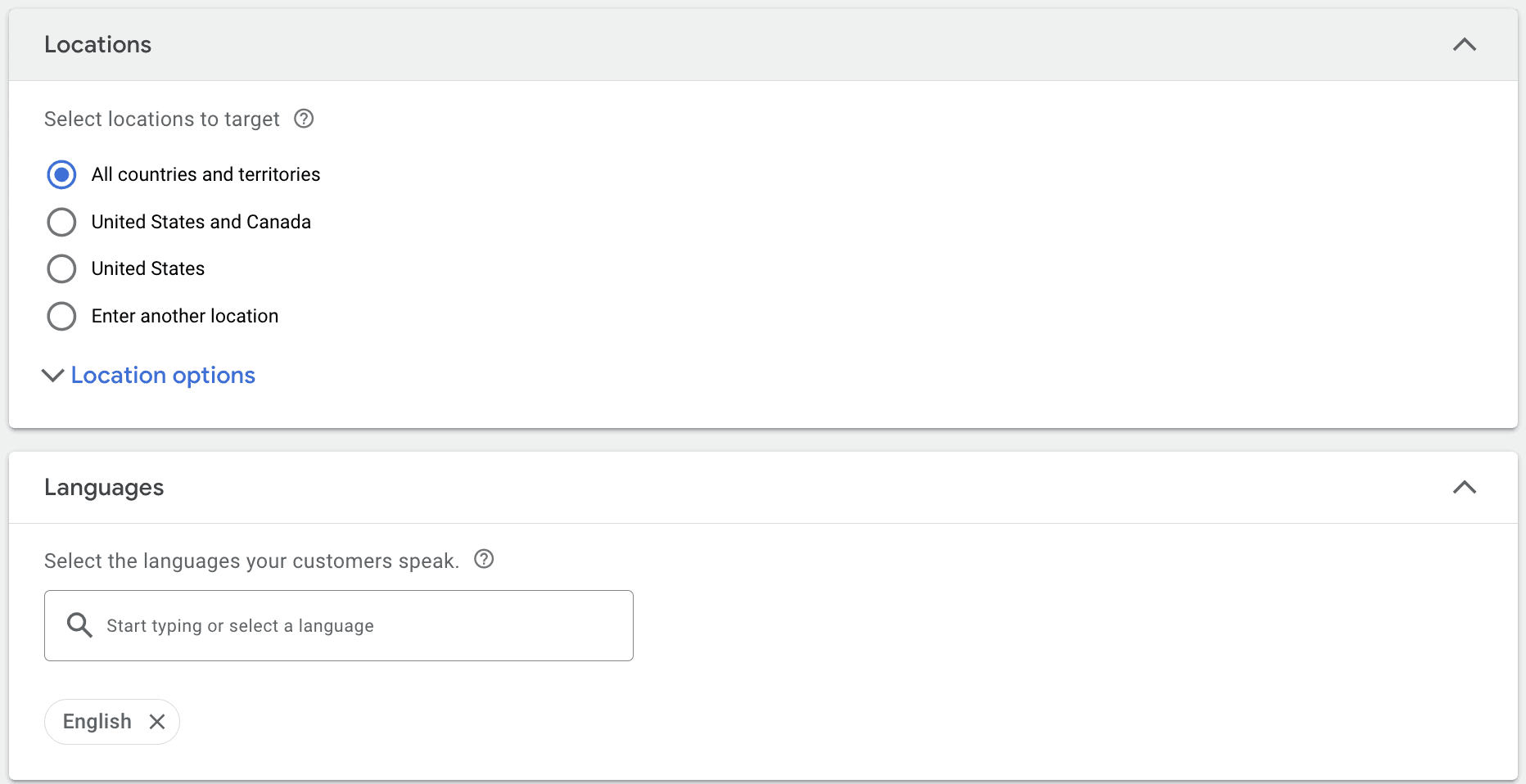
You can also choose if you want to reach people who are currently in or regularly in the targeted area or if you also want to reach people who are in, regularly in, or also shown interest in your targeted areas.

Finally, choose the languages that your customers speak. Remember that it’s best to create segmented campaigns that will show ads to users in their preferred language when possible.
Audience Segments
Next, we have a particularly powerful type of audience targeting category: Audience segments.
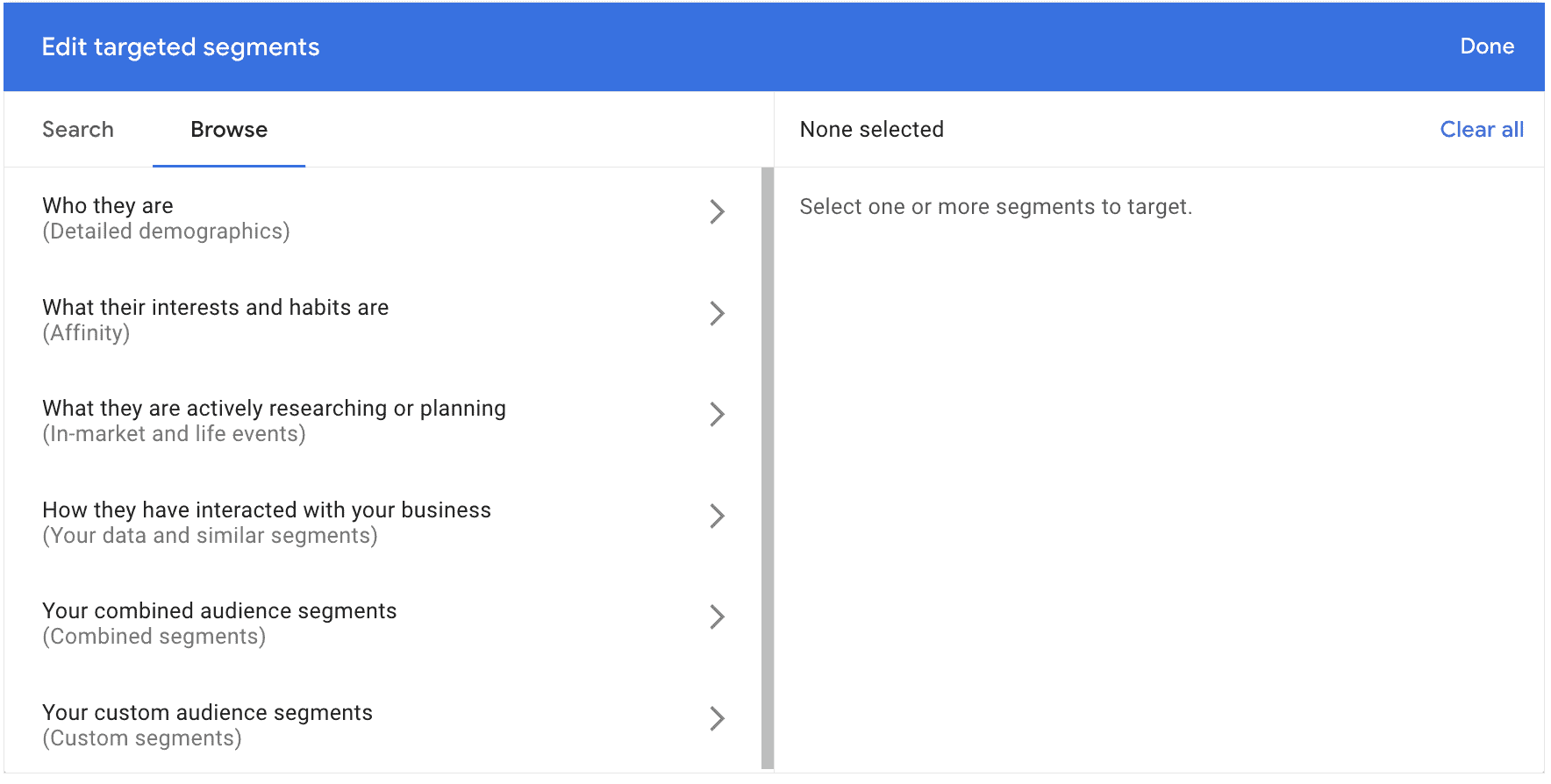
Audience segments allow you to reach a number of different types of audience segments based on traits they have in common, including the following:
- Detailed demographics, like whether they’re homeowners, parents, or college graduates
- Interests and habits, like whether they’re bargain hunters or luxury shoppers or if they’re regularly business travelers
- What they’re actively researching or planning, like if they’re looking for a job, they’re buying a home, or they’re actively in the market for different goods or services
- How they’ve interacted with your business, which includes remarketing options like visiting your website or watching a YouTube video
- Combined and custom audience segments, which allow you to create stacked audiences that you can quickly access
This may be more of the most useful audience targeting categories available. The remarketing features, in particular, are dead useful, allowing you to reach users who are already somewhere in your buyer’s funnel with hyper-targeted ads. Make sure you read our chapter on Remarketing Campaigns in Google Display Ads to take full advantage of this feature.
Knowing what users are in the market for and what they’re interested in can go a long way in reaching the right people with your ad.
Realtors, for example, can target users who are in the market to buy a home, as can painters, landscapers, and cleaning companies, since all of these services are often used not long after a home is purchased.
A curly hair company can target users who are researching different beauty products.
You can also use these ads to ensure that you’re creating niche messaging and creatives that will jump out at your target audience.
If I’m trying to sell a Roomba-style automated cleaning system, I could create different audience segments with messaging that’s incredibly relevant to them. See these examples:
- For business owners, I’d use copy like “You’re busy running your business. We can run the cleaning.”
- For parents, I’d use copy that stresses that there’s always a mess to clean but that we can handle it while you make memories with your children
- And for pet owners, I’d talk about how we can help you avoid the dreaded tumbleweeds of pet hair
There are plenty of ways to use targeting options within the audience segments category, so take advantage of them as relevant!
Demographics
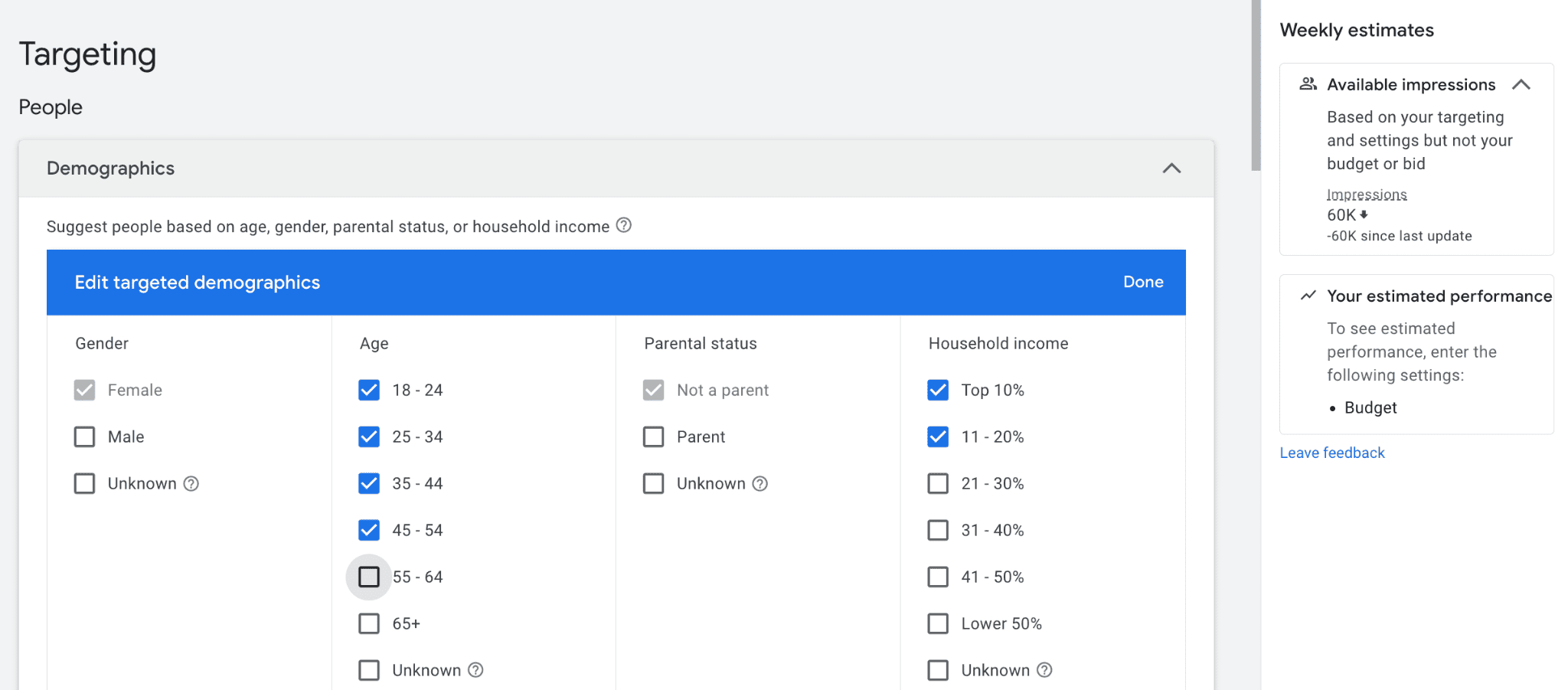
Demographics are straightforward with Google Display Ads. You can choose to target by gender, age range, parental status, and household income. Household income is only available in some countries, so may not be an option for all audiences.
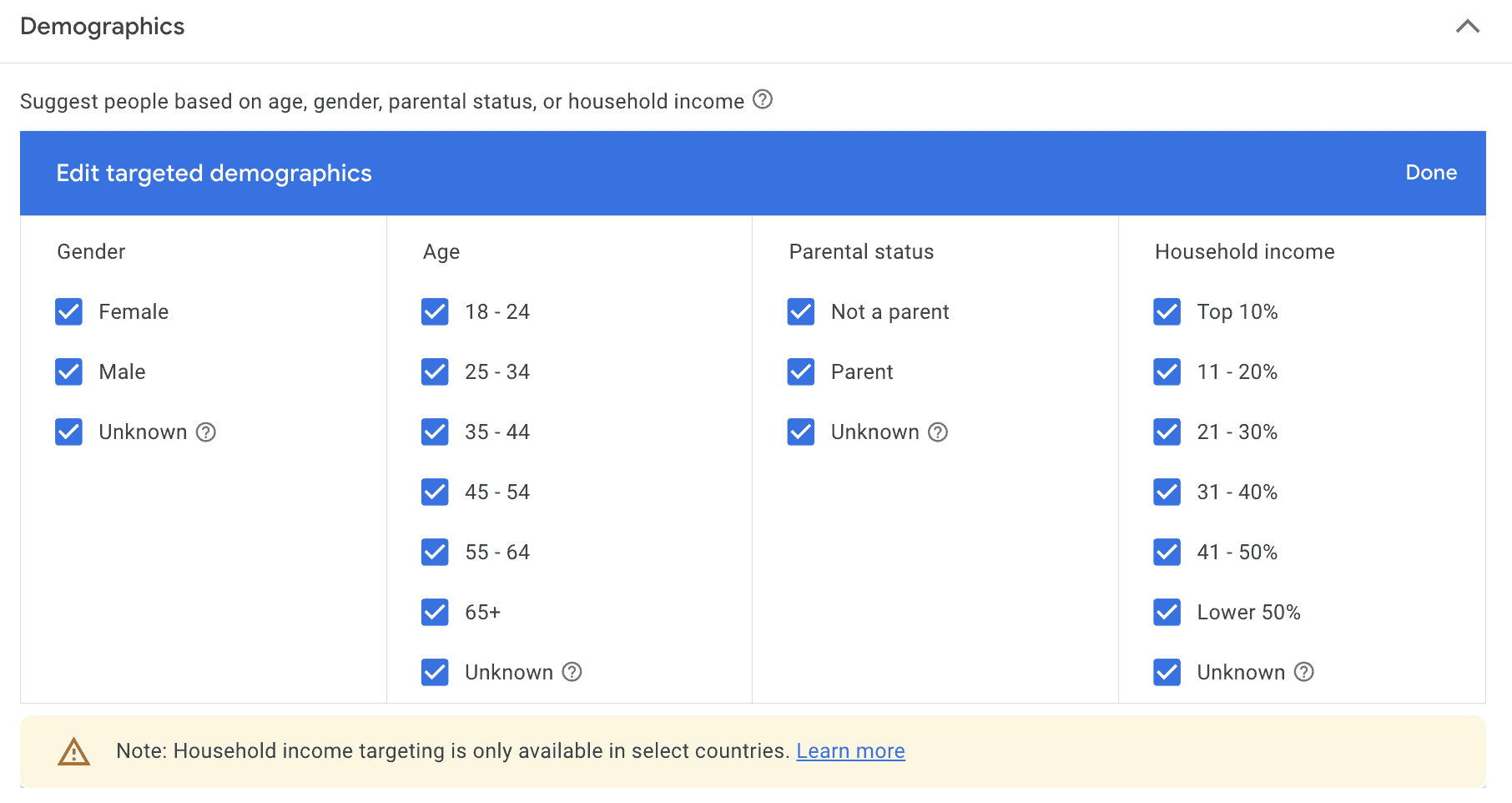
With demographic targeting, all options are automatically enabled, so you’ll need to disable the audiences you don’t want to reach. Even if you only want to exclude a single and very small segment of users (like users age 65+), it can help eliminate irrelevant views.
Demographic information may not necessarily seem as useful as interest or behavior targeting when you’re trying to cast a wide net, but for some campaigns, it can put you in front of the right audience. And it can certainly help make sure you don’t end up in front of the wrong audience.
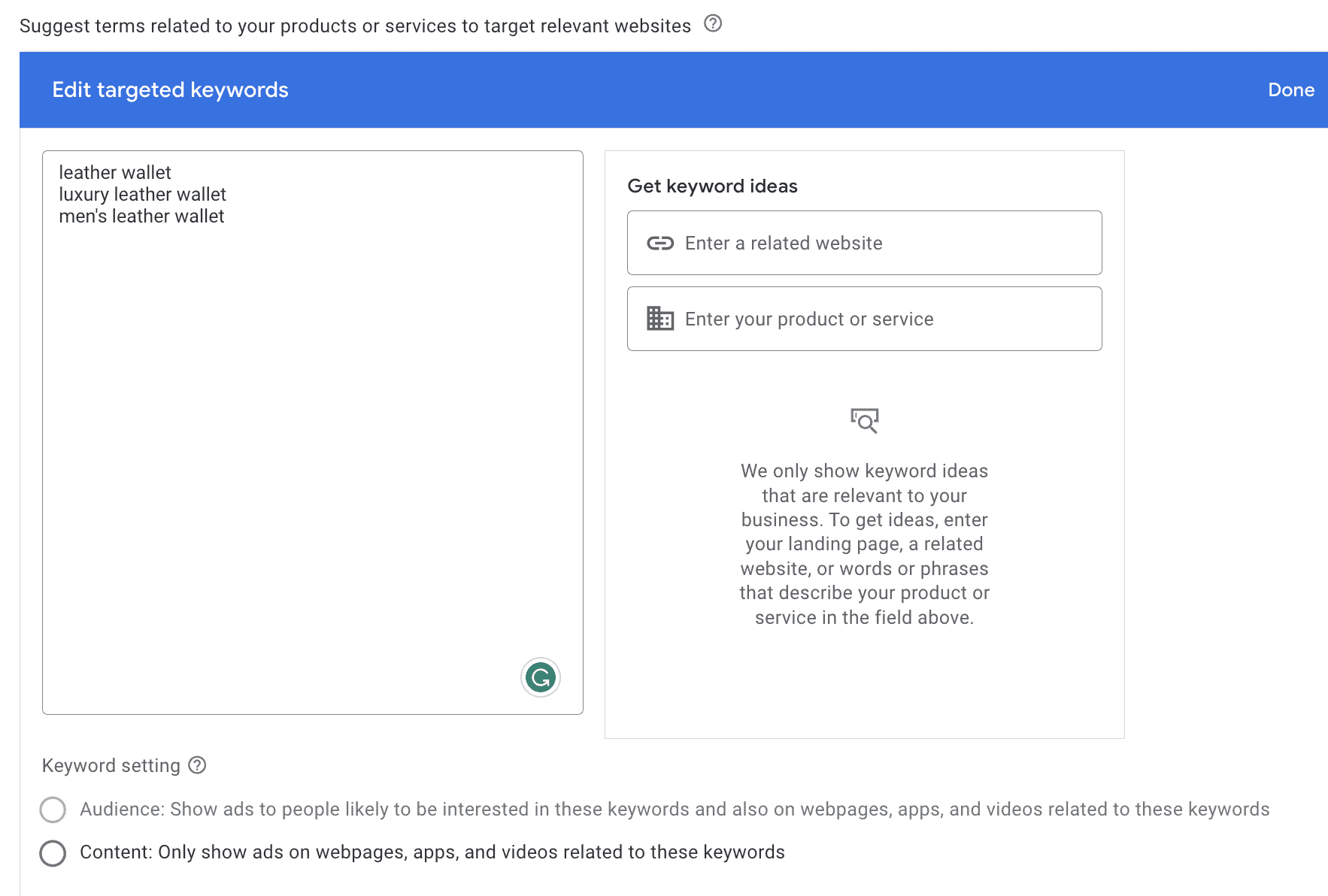
Keywords
The keywords targeting category is an interesting one. You can enter a list of keywords manually or get ideas based on a related website or your product or service.
You can then either choose to:
- Target audiences to people who are likely to be interested in your selected keywords and webpages, apps, and videos related to those keywords
- Only show ads on webpages, apps, and videos related to the keywords
This is different than the other categories we’ve looked at because a big focus is on relevant placements even more than relevant audience characteristics. In theory, this can help you reach users when they’re in the right frame of mind, like showing them an ad for a blender on a site for cocktail recipes. This may increase your chance of conversions.
You can, of course, also show your ads to users likely to be interested in the specified keywords regardless of (or in addition to) relevant placements.
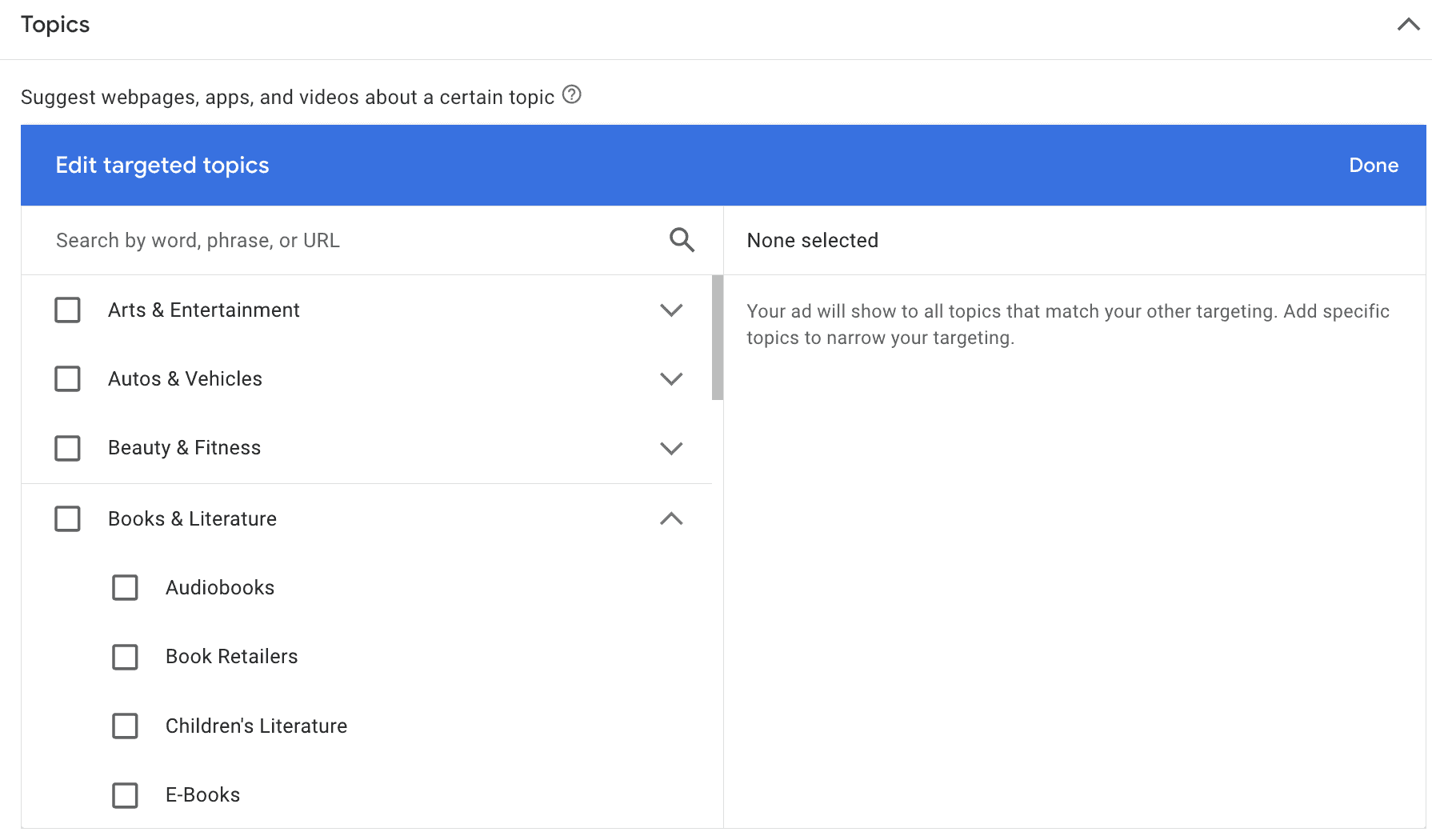
Topics
Topics are another placement-focused targeting option. The goal here is to choose the topics of websites, apps, or videos that you want your ad to be shown on, and the idea is the same as above; right place, right time. It can be particularly useful for reaching users during the discovery phase of the digital sales funnel.
You can browse for topics or search for them. Browsing can give you a ton of ideas because there are likely topics here that are incredibly specific that you may not have thought of.
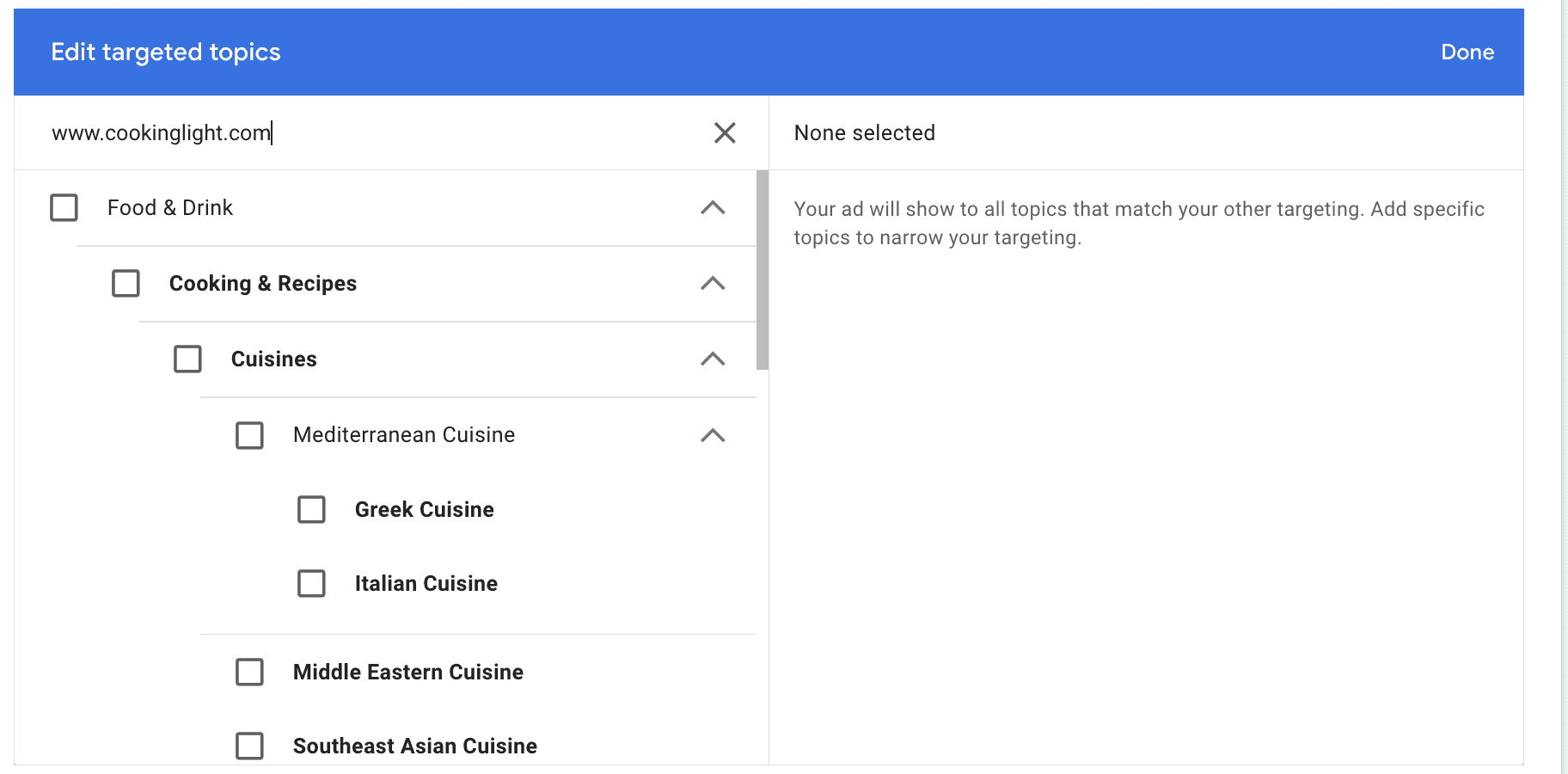
You also have the option of entering a specific site URL. This will search the site and suggest all the different topics that users who visit that site have, making it a great way to add similar keywords to your campaign without limiting yourself to a single placement if you don’t want to.
Placements
Finally, for the audience targeting options that aren’t made up of established custom audiences, we’ve got placements.
Placements allow you to choose specific websites, videos, or apps where you want your ad to appear. If your website has an equivalent app, your ads can appear there as well.
If you know that certain websites are full of high-value members of your target audience, this is an outstanding placement to try. You can enter a specific website or browse based on keywords or topics.

One thing to note is that this may be an audience type that you want to test separately from your main audience targeting options in an A/B test. This can really narrow down your overall reach, so it’s great for a niche campaign, but it can otherwise limit you if you want to definitely reach users on this site, but you also want to reach users elsewhere.
What About Audience Layering?
So one important thing to note: You don’t have to choose just a single audience targeting criteria. And in many cases, you don’t necessarily want to.
This is called audience layering, and it involves stacking different audience targeting options on top of each other.
You can create a remarketing audience off of people who visited your site and then narrow it down further by showing the ad only to users who frequently make luxury purchases.
Or you can choose placements as a core targeting option and then add demographic and audience segment targeting options on top of that.
You do want to be careful with audience layering; it can help you refine an audience like nothing else, but you can narrow it down too much. If this happens, you could be looking at exceptionally high costs per action (CPAs), and it can cause a massive hit on potential reach. We’ll talk more about this a little later on.
How to Navigate the Display Ads Targeting System
Navigating the ads targeting system is fairly simple and straightforward, and a little playing around with it will help you become familiar with the options available.
First, you’ll see the list of different targeting options all in one place. Click on the one that you’re interested in adding to your campaign.
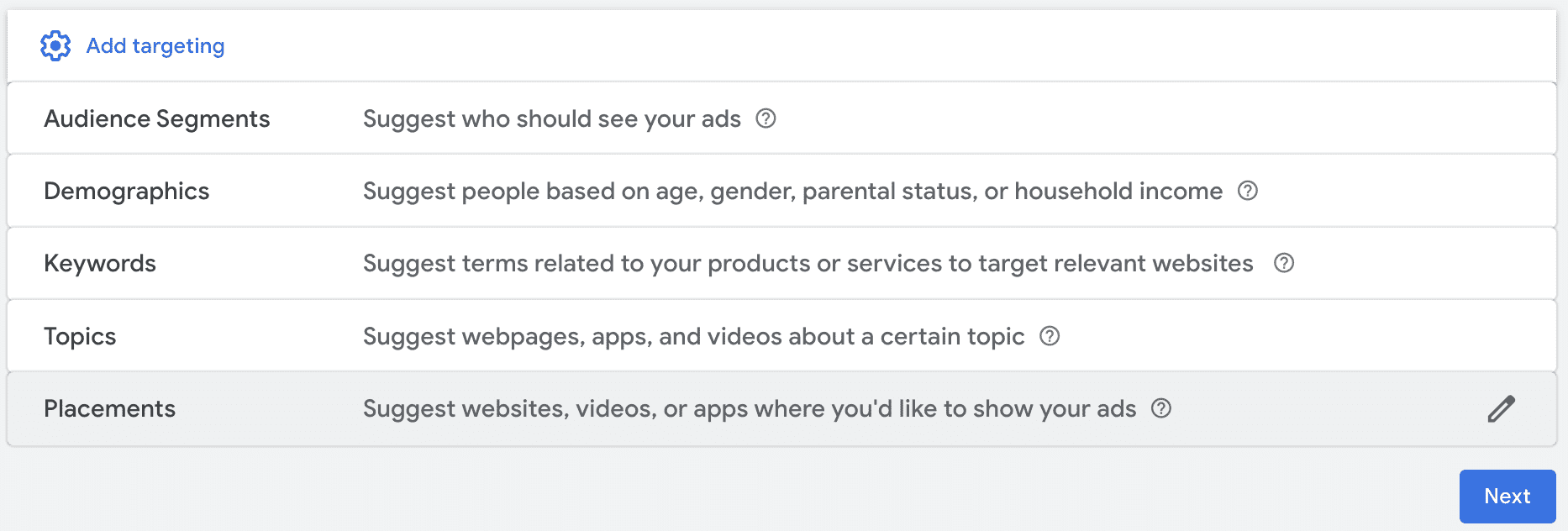
Most of them will open a drop-down menu that allows you to search or browse for specific criteria, and then you can select whichever matches your campaigns.
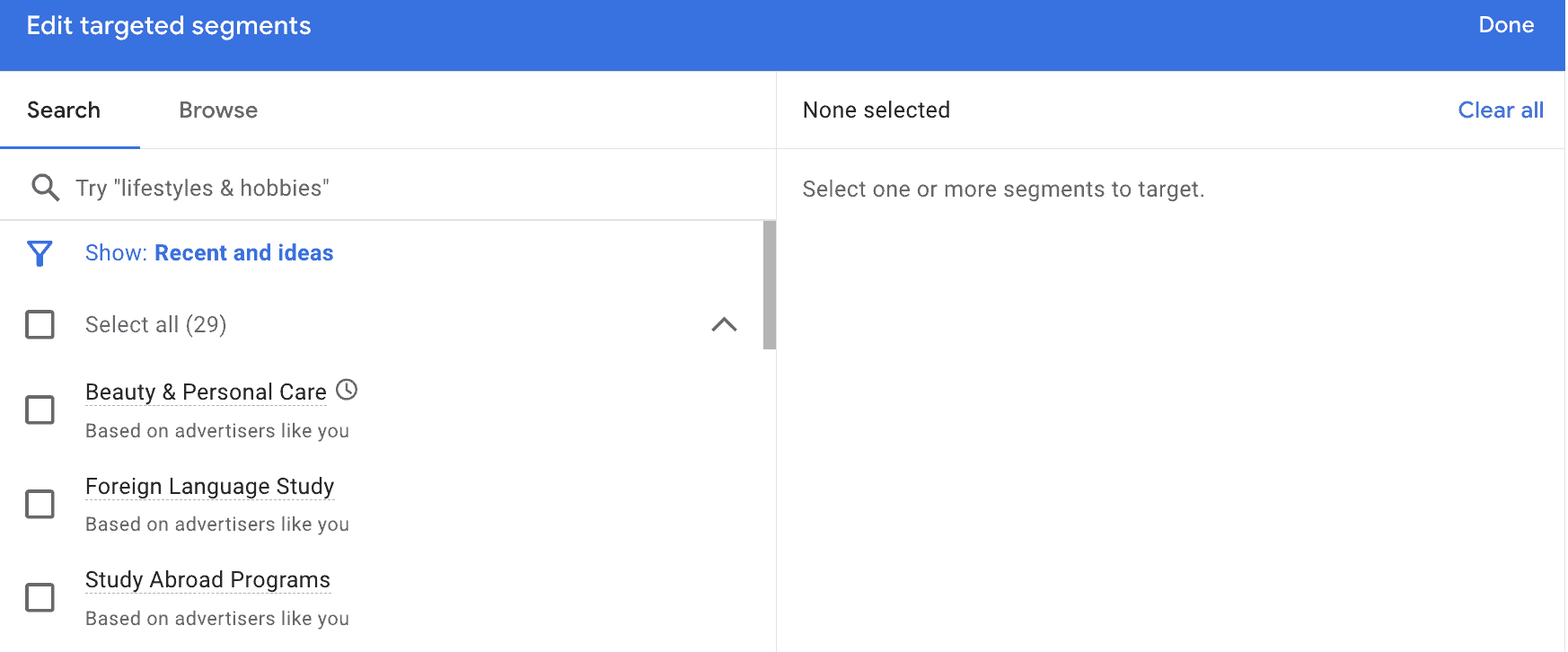
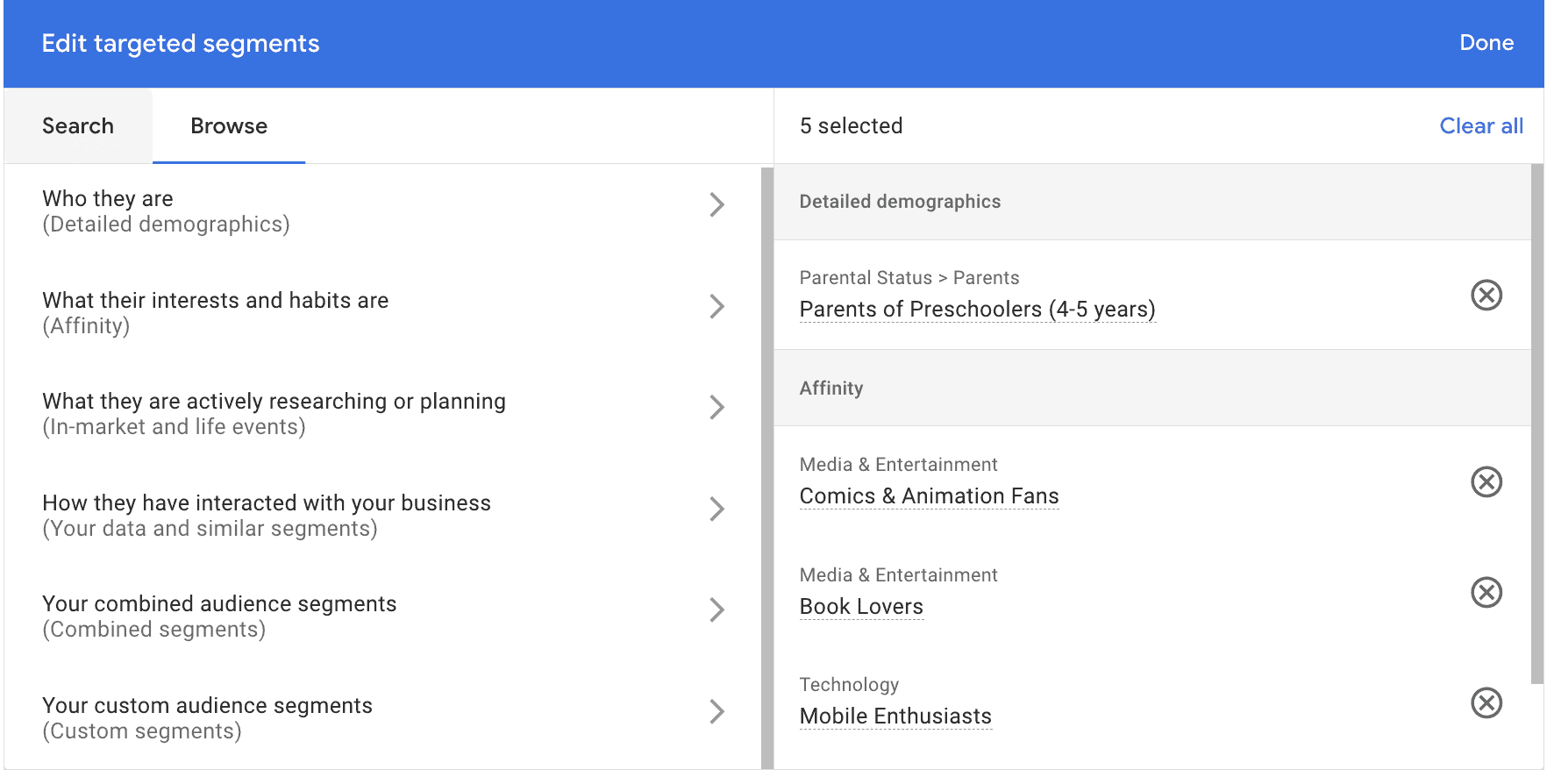
You can add multiple options from each category and some from different categories. (We’ll talk about this more in a minute).
![]()
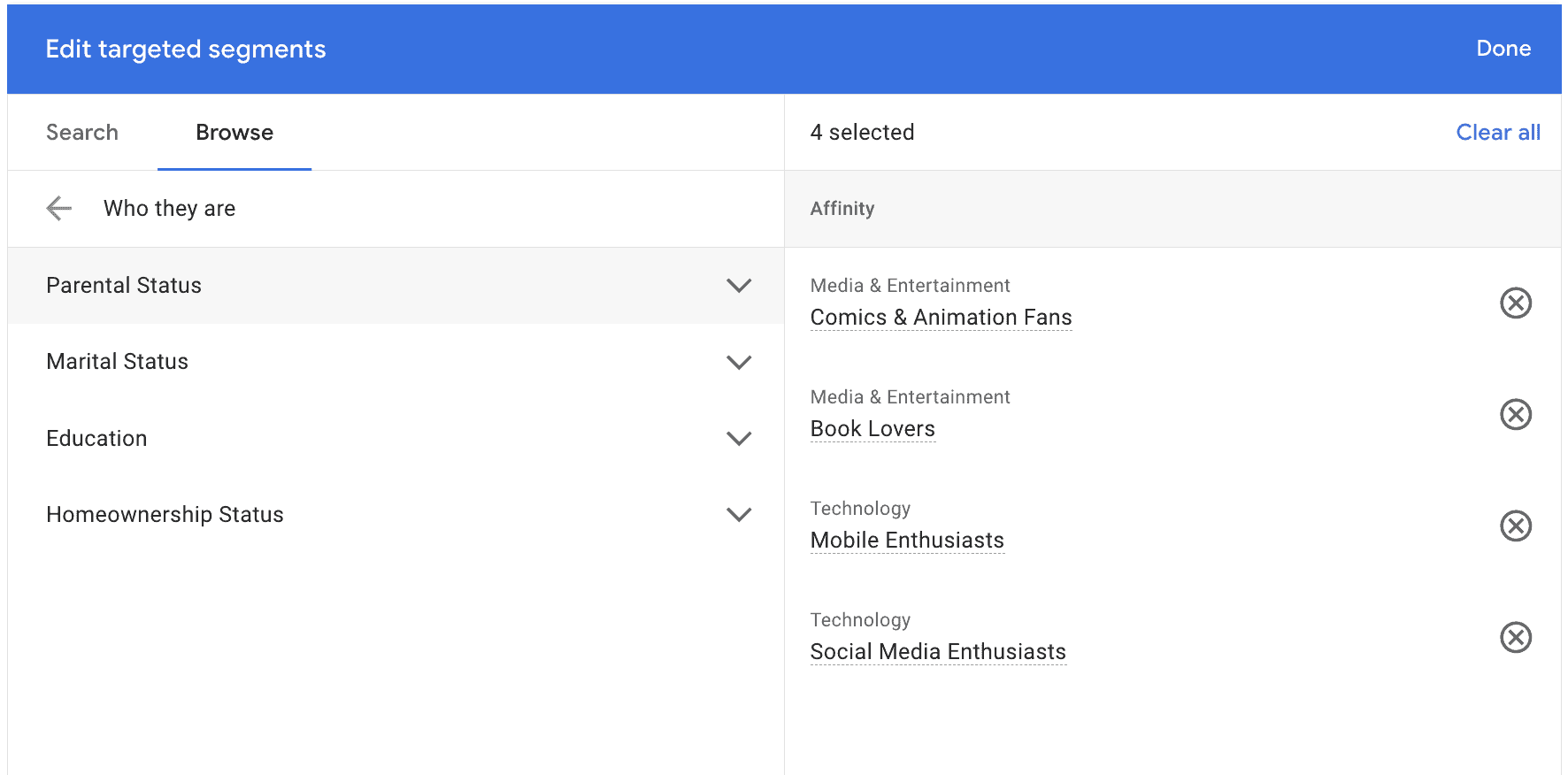
When you’re done with one category (like targeted segments and you’re ready to move to another, like interests), click Done and move to the next.
Once your audience is where you want it to be, take a look at those helpful “weekly estimates” on the right side of the targeting page. It will give you a basic idea of how your audience targeting is impacting reach, and you want to avoid having it become too narrow.
How to Choose an Audience Targeting Strategy That Works for You
Ready to get started creating an audience targeting strategy that will help you reach the right people? Let’s take a look at some of the steps we use in our strategy for clients.
1. Think About What Audience You Want to Reach for Each Campaign
It’s so easy to go in with little or no plan and end up dazzled by the different options. You want to go in with a clear strategy so that you’re only choosing the right audience targeting options for the specific campaign in question.
Ask yourself this about the audience you want to reach with the specific campaign you’re working on:
- What do they have in common?
- Which audience segments could you break that already-segmented audience into? (ie, parents vs. non-parents)
- What messaging would appeal to each individual niched-down segment?
2. Consider the Stage of the Sales Funnel You Want to Reach
This is incredibly important. What stage of the digital sales funnel are you most hoping to reach with your campaign?
Do you want to reach cold audiences? Existing customers with an upsell offer? Warm leads who haven’t converted yet, or abandoned cart users?
Knowing this will help you determine whether or not to incorporate remarketing and consider the right copy and offers to use.
3. Find the Right Balance
A lot of marketing is about balance, and Google Display Ads targeting is no different.
You want to create an audience that isn’t so broad that you struggle to connect with the right people, but you absolutely don’t want to create an audience too narrow that costs go up and you’re accidentally excluding a large chunk of the audience segment.
Testing can help you find the right balance.
And keep in mind that Google’s optimization is pretty phenomenal. Given a few weeks (depending on your budget), they can start to learn which users and placements are driving the most clicks and conversions, and they’ll optimize for those. Providing Google with a good starting point and some rules is helpful, but don’t box yourself in too much.
4. Test for At Least Two Weeks
If you’re running a dedicated A/B test, you should be running your campaigns for a minimum of two weeks before switching them off unless it’s an absolute crash-and-burn scenario. Google takes a little time to find its groove and to really understand exactly who it should be showing the ad to, so it takes around two weeks for the average budget.
Final Thoughts
Audience targeting is essential to the success of your Google Display Ad campaigns, so it’s important to get it right, whether that means more or less targeting and choosing which options to use.
This is one of the most complex parts of Google Ads outside of the creatives themselves, so testing is important. And if you’re still struggling to see results, get in touch with an ad agency with experience— we can help you there.
Need help with your Google Ad campaigns? Learn more about what makes our agency different here.



 How to Create Google Display Remarketing Campaign
How to Create Google Display Remarketing Campaign
